Which Step in Translation Initiation Is Unique to Eukaryotes
This makes up the initiation complex. BThe initiation complex moves the small ribosomal subunit through the 5 UTR scanning for the start AUG.
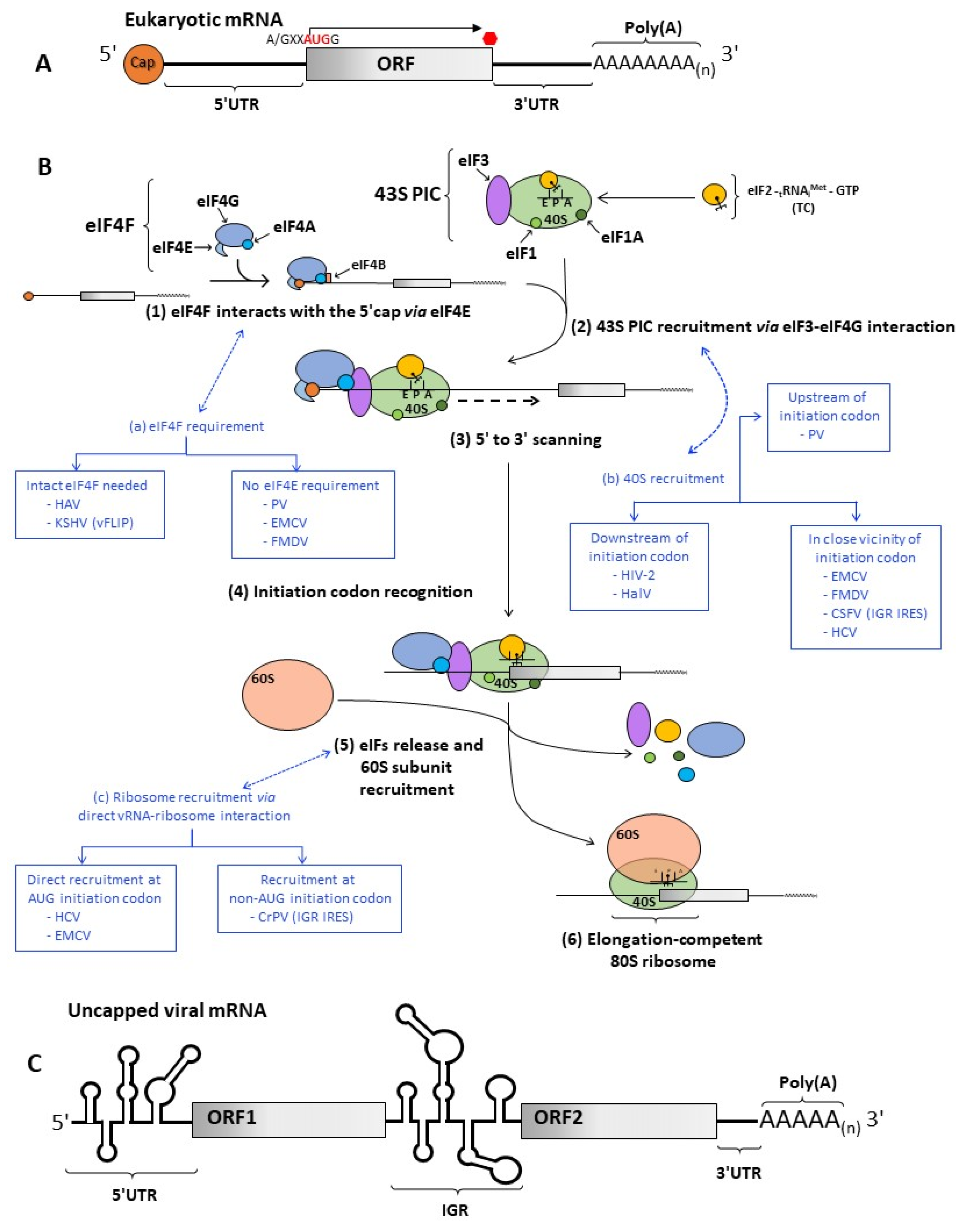
Viruses Free Full Text Rna Binding Proteins As Regulators Of Internal Initiation Of Viral Mrna Translation Html
The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. The pathway for recruiting initiator transfer RNA tRNA to the messenger RNA mRNA AUG codon in the context of an 80S ribosome bottom right is depicted as a series of major steps labeled with blue text linked with black arrows. Coli a representative prokaryote and specify any differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation.
Here well explore how translation occurs in E. Initiation elongation and termination. The first step is the formation of a pre-initiation complex consisting of the 40S small ribosomal subunit Met-tRNA i met eIF-2 and GTP.
Biology questions and answers. In bacteria translation initiation involves the interaction of the mRNA with the ribosomal small subunit. The N-formylated methionine is chain initiating.
Before going through Eukaryotic Translation steps please take a look at our previous article Prokaryotic Translation Steps Requirements to check the components required for the translation procedure. Interestingly the proteins carrying these unique modifications are all involved in the elongation steps of. The mRNA is synthesized from DNA only.
Many eukaryotic mRNAs are translated from the first AUG but this is not always the case. The activation of aminoacids take place in cytosol. Prokaryotic translation basically occurs in three steps.
This constraint on the initiation step of translation in eukaryotes dictates the location of transcriptional promoters and may have contributed to the evolution of splicingThe binding of Met-tRNA to ribosomes is mediated by a GTP-binding protein in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but the more complex structure of the eukaryotic factor eIF-2. In eukaryotes translation also occurs in ribosome located on the Endoplasmic Reticulum ER. O translocation of the ribosome in the 3 direction O formation of the initiation complex binding of ribosomes to the 5 cap of the mRNA O formation of the preinitiation complex O ribosome assembly Submit Request Answer.
The pre-initiation complex binds to the 5 end of the eukaryotic mRNA a step that requires eIF. In eukaryotic organisms translation also occurs in three phases that include initiation elongation and termination. Initiation of translation usually involves the interaction of certain key proteins the initiation factors with a special tag bound to the 5-end of an mRNA molecule the 5 cap as well as with the 5 UTRThese proteins bind the small 40S ribosomal subunit and hold the mRNA in place.
Eukaryotic translation initiation is the most. This step completes the initiation of translation in eukaryotes figure 118. Translation initiation in eukaryotes - This lecture explains about the initiation of translation in eukaryotes.
Many diseases including cancer and metabolic disorders are connected with improper functioning or regulation of the initiation of. Initiation elongation and termination. Ribosomes are made of a small and large subunit which surrounds the mRNA.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. Translation initiation is a key step for regulating the synthesis of several proteins. Initiation elongation and termination.
In contrast eukaryotes have evolved a sophisticated mechanism that relies mostly on protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions. Eukaryotic 40s ribosomal subunit complexes with eukaryotic initiation factor proteins and with charged tRNAmet. In prokaryotes this process involves the direct interaction of the ribosomal RNA with the mRNA.
In prokaryotic translation 70S ribosomes with 30S and 50S subunits are used. Step 2 eukaryotic translation initiation. 7Elongation factors translocate the ribosome in the 3 direction by.
Here well explore how translation occurs in E. Steps in translation. Eukaryotes require transcription factors to first bind to the promoter region and then help recruit the appropriate polymerase.
Once the appropriate AUG is identified the other proteins and CBP dissociate and the 60S subunit binds to the complex of Met-tRNAi mRNA and the 40S subunit. The key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation initiation is that prokaryotic translation initiation occurs on 70S ribosomes while eukaryotic translation initiation occurs on 80S ribosomes. Translation or protein synthesis is a biological process that takes place in the cytoplasm.
In translation messenger RNA mRNA is decoded to produce a specific polypeptide according to the rules specified by the genetic code. RNA Polymerase II is the polymerase responsible for transcribing mRNA. Translation Initiation in Eukaryotes Translation initiation is the target of regulation in a number of cellular processes including development differentiation stress response and neuronal function.
In eukaryotes there is single initiation and termination site. Overview of the general eukaryotic translation initiation pathway. These modifications occur on eukaryotic elongation factor 1A eEF1A eukaryotic initiation factor 5A eIF5A and eukaryotic elongation factor 2 eEF2 respectively.
Preinitiation complex recruited to 5-cap reigion of mRNA. Step 1 eukaryotic translation initiation. Part A Which step in translation initiation is unique to eukaryotes.
Coli a representative prokaryote and specify any differences between. The activation of aminoacids is catalyzed by their aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. The initiation of protein synthesis consists in the recruitment of a ribosomeinitiator tRNA complex to the initiation codon of a messenger RNA.
In prokaryotes there are several initiation and termination sites. 8Which step in translation initiation is unique to eukaryotes. Additionally translation initiation factors 1 2 and 3 and the initiator tRNA also assemble on the ribosomal small subunit and are essential for.
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm where the ribosomes are located. While this is similar to the process in prokaryotes there are several differences particularly with regards to the components. Individual eukaryotic initiation factor eIF.
All the 20 aminoacids are activated and bound to 3 end of their specific tRNA in the presence of ATP and Mg. EIF3 is associated with the 40S ribosomal subunit and plays a role in keeping the large 60S. It proceeds via three steps.
Eukaryotic transcription is carried out in the nucleus of the cell and proceeds in three sequential stages. The three initiation factors IF1 IF2 and IF3 help to assemble the initiation complex. Outline the basic steps of translation.
In eukaryotic translation 80S ribosomes with 40S and 60S subunits are used. Initiation elongation and termination. The mRNA is synthesized from DNA only.
As with mRNA synthesis protein synthesis can be divided into three phases. In order to initiate the translation the two subunits 50S and 30S are assembled. The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Preinitiation complex joins eIF4 complex.

Pin On Genetics Molecular Biology

What Is The First Step Of Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Ap Biology Teaching Chemistry

Measurements Of Microbial Growth In 2021 Microbial Microbiology Growth Medium

Simplified Scheme Of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation With Steps Download Scientific Diagram
Model For Two Gtp Dependent Steps In Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Download Scientific Diagram

The Formation Of The Basic Translation Initiation Complex In Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Representation Of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Step I Download Scientific Diagram

Global And Specific Regulation Of Translation Initiation A Overview Download Scientific Diagram
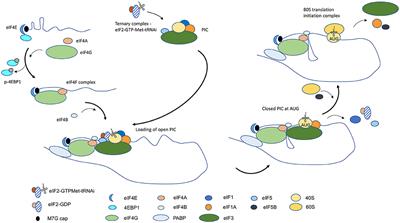
Disorder At The Start The Contribution Of Dysregulated Translation Initiation To Cancer Therapy Resistance Oral Health Frontiers
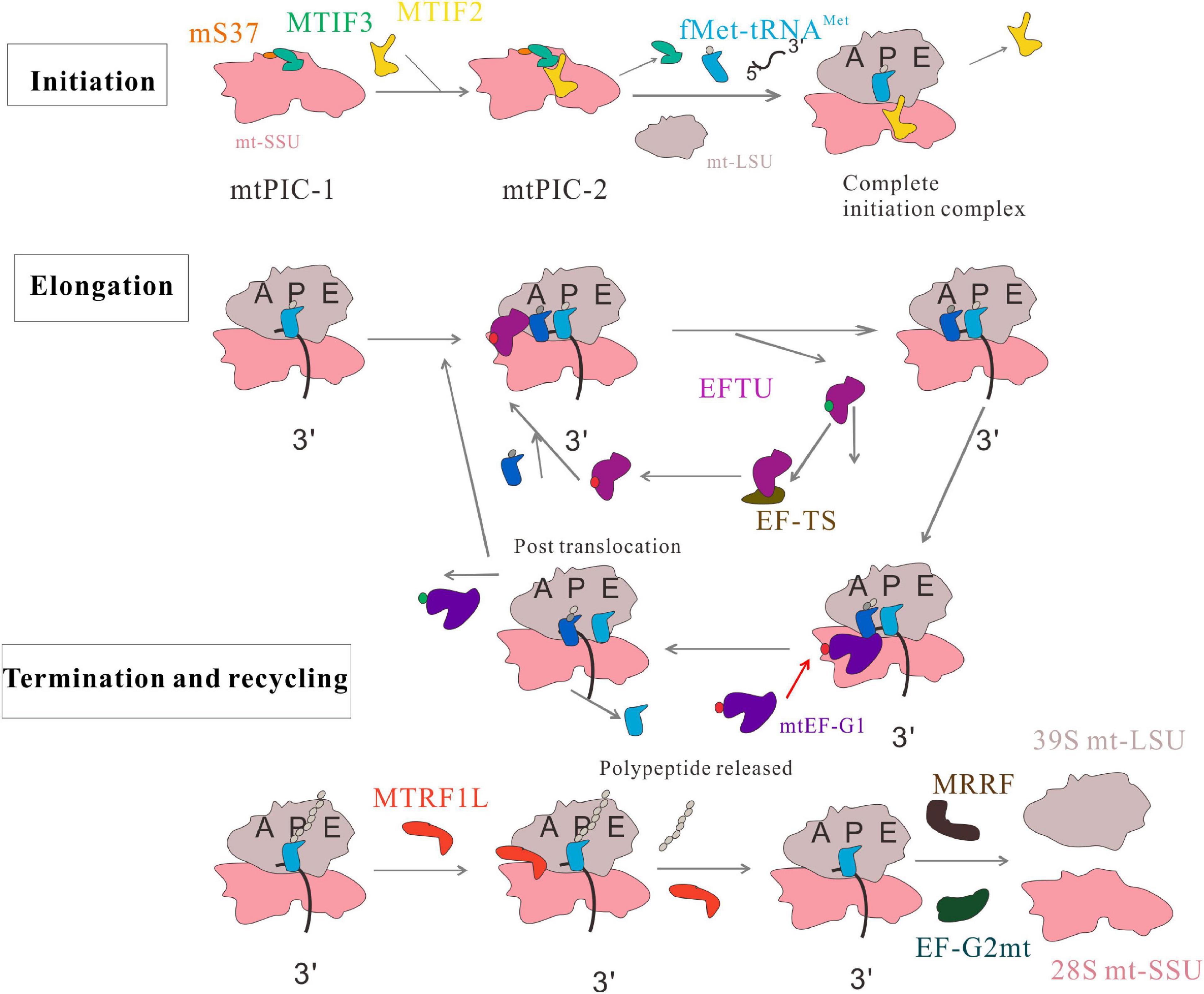
Frontiers Mitochondrial Protein Translation Emerging Roles And Clinical Significance In Disease Cell And Developmental Biology

Translation Description Process Location Britannica

Schematic Representation Of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Step I Download Scientific Diagram

Translation Initiation In Eukaryotes Translation Of Most Eukaryotic Download Scientific Diagram

Protein Synthesis Steps Protein Synthesis Biology Projects Protein Synthesis Protein

Dna Codon Table Brain Facts Protein Synthesis Dna Transcription

Schematic Diagram Of Translation Initiation In Eukaryotes Translation Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Diagram Of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Translation Download Scientific Diagram

The Eukaryotic 80 S Initiation Pathway A General Scheme For The Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment